Contents
【問題】
【難易度】★★☆☆☆(やや易しい)
三相\( \ 3 \ \)線式交流送電線があり,電線\( \ 1 \ \)線当たりの抵抗が\( \ R \ \mathrm {[\Omega ]} \ \),受電端の線間電圧が\( \ V_{\mathrm {r}} \ \mathrm {[V]} \ \)である。今,受電端から力率\( \ \cos \theta \ \)の負荷に三相電力\( \ P \ \mathrm {[W]} \ \)を供給しているものとする。
この送電線での\( \ 3 \ \)線の電力損失を\( \ P_{\mathrm {L}} \ \)とすると,電力損失率\( \ \displaystyle \frac {P_{\mathrm {L}}}{P} \ \)を表す式として,正しいものを次の(1)~(5)のうちから一つ選べ。
ただし,線路のインダクタンス,静電容量及びコンダクタンスは無視できるものとする。
(1) \( \ \displaystyle \frac {RP}{3\left( V_{\mathrm {r}}\cos \theta \right) ^{2}} \ \) (2) \( \ \displaystyle \frac {RP}{\left( V_{\mathrm {r}}\cos \theta \right) ^{2}} \ \) (3) \( \ \displaystyle \frac {RP^{2}}{\left( V_{\mathrm {r}}\cos \theta \right) ^{2}} \ \)
(4) \( \ \displaystyle \frac {3RP}{\left( V_{\mathrm {r}}\cos \theta \right) ^{2}} \ \) (5) \( \ \displaystyle \frac {3RP^{2}}{\left( V_{\mathrm {r}}\cos \theta \right) ^{2}} \ \)
【ワンポイント解説】
三相\( \ 3 \ \)線式交流送電線の電力損失率を求める問題です。
重要公式である電力の公式\( \ P =\sqrt {3}V_{\mathrm {r}}I\cos \theta \ \)と電力損失\( \ P_{\mathrm {L}} =3rI^{2} \ \)を組み合わせて導出します。
計算慣れのような問題なので,ぜひ本問で理解するようにして下さい。
本問は平成19年問10からの再出題となります。
1.送電線の送電電力と電力損失
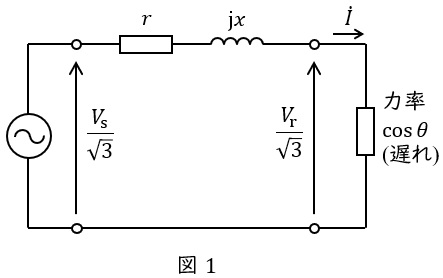
送電端の電圧が\( \ V_{\mathrm {s}} \ \mathrm {[V]} \ \),受電端の電圧が\( \ V_{\mathrm {r}} \ \mathrm {[V]} \ \),送電線の\( \ 1 \ \)線あたりの抵抗が\( \ r \ \mathrm {[\Omega ]} \ \),リアクタンスが\( \ x \ \mathrm {[\Omega ]} \ \),送電線に流れる電流が\( \ I \ \mathrm {[A]} \ \),負荷の力率が\( \ \cos \theta \ \)であるとすると,送電線の一相分等価回路は図1のように描くことができます。
このとき,負荷電力\( \ P \ \mathrm {[W]} \ \)は,
\[
\begin{eqnarray}
P &=&\sqrt {3}V_{\mathrm {r}}I\cos \theta \\[ 5pt ]
\end{eqnarray}
\]
となり,上式より,
\[
\begin{eqnarray}
I &=&\frac {P}{\sqrt {3}V_{\mathrm {r}}\cos \theta } \\[ 5pt ]
\end{eqnarray}
\]
であるため,送電線での電力損失\( \ P_{\mathrm {L}} \ \mathrm {[W]} \ \)は,
\[
\begin{eqnarray}
P_{\mathrm {L}} &=&3rI^{2} \\[ 5pt ]
&=&3r\left( \frac {P}{\sqrt {3}V_{\mathrm {r}}\cos \theta }\right) ^{2} \\[ 5pt ]
&=&\frac {P^{2}r}{V_{\mathrm {r}}^{2}\cos ^{2}\theta } \\[ 5pt ]
\end{eqnarray}
\]
となります。
【解答】
解答:(2)
送電線での電力損失\( \ P_{\mathrm {L}} \ \mathrm {[W]} \ \)は,ワンポイント解説「1.送電線の送電電力と電力損失」の通り,
\[
\begin{eqnarray}
P_{\mathrm {L}} &=&\frac {RP^{2}}{V_{\mathrm {r}}^{2}\cos ^{2}\theta } \\[ 5pt ]
\end{eqnarray}
\]
であるから,電力損失率\( \ \displaystyle \frac {P_{\mathrm {L}}}{P} \ \)は,
\[
\begin{eqnarray}
\frac {P_{\mathrm {L}}}{P} &=&\frac {\displaystyle \frac {RP^{2}}{V_{\mathrm {r}}^{2}\cos ^{2}\theta }}{P} \\[ 5pt ]
&=&\frac {RP}{\left( V_{\mathrm {r}}\cos \theta \right) ^{2}} \\[ 5pt ]
\end{eqnarray}
\]
と求められる。






















 愛知県出身 愛称たけちゃん
詳しくは
愛知県出身 愛称たけちゃん
詳しくは